Factory Pattern
Factory pattern is one of most used design pattern in Java. This type of design pattern comes under creational pattern as this pattern provides one of the best ways to create an object.
In Factory pattern, we create object without exposing the creation logic to the client and refer to newly created object using a common interface.
Implementation
We're going to create a Shape interface and concrete classes implementing the Shape interface. A factory class ShapeFactory is defined as a next step.
FactoryPatternDemo, our demo class will use ShapeFactory to get a Shape object. It will pass information (CIRCLE / RECTANGLE / SQUARE) to ShapeFactory to get the type of object it needs.
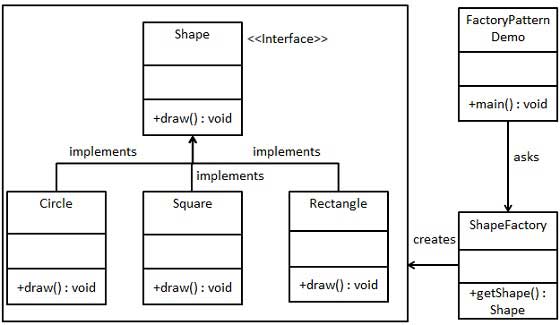
Step 1
Create an interface.
Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
Step 2
Create concrete classes implementing the same interface.
Rectangle.java
public class Rectangle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
Square.java
public class Square implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method.");
}
}
Step 3
Create a Factory to generate object of concrete class based on given information.
ShapeFactory.java
public class ShapeFactory {
//use getShape method to get object of type shape
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
if(shapeType == null){
return null;
}
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){
return new Circle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){
return new Rectangle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")){
return new Square();
}
return null;
}
}
Step 4
Use the Factory to get object of concrete class by passing an information such as type.
FactoryPatternDemo.java
public class FactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory();
//get an object of Circle and call its draw method.
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
//call draw method of Circle
shape1.draw();
//get an object of Rectangle and call its draw method.
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
//call draw method of Rectangle
shape2.draw();
//get an object of Square and call its draw method.
Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");
//call draw method of circle
shape3.draw();
}
}
Step 5
Verify the output.
Inside Circle::draw() method.
Inside Rectangle::draw() method.
Inside Square::draw() method.
工厂方法模式分为三种:
1.1、普通工厂模式,就是建立一个工厂类,对实现了同一接口的一些类进行实例的创建。首先看下关系图:

举例如下:(我们举一个发送邮件和短信的例子) 首先,创建二者的共同接口:
public interface Sender {
public void Send();
}
其次,创建实现类:
public class MailSender implements Sender {
@Override
public void Send() {
System.out.println("this is mailsender!");
}
}
public class SmsSender implements Sender {
@Override
public void Send() {
System.out.println("this is sms sender!");
}
}
最后,建工厂类:
public class SendFactory {
public Sender produce(String type) {
if ("mail".equals(type)) {
return new MailSender();
} else if ("sms".equals(type)) {
return new SmsSender();
} else {
System.out.println("请输入正确的类型!");
return null;
}
}
}
我们来测试下:
public class FactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SendFactory factory = new SendFactory();
Sender sender = factory.produce("sms");
sender.Send();
}
}
输出:
this is sms sender!
1.2、多个工厂方法模式,是对普通工厂方法模式的改进,在普通工厂方法模式中,如果传递的字符串出错,则不能正确创建对象,而多个工厂方法模式是提供多个工厂方法,分别创建对象。关系图:

将上面的代码做下修改,改动下SendFactory类就行,如下:
public class SendFactory {
public Sender produceMail(){
return new MailSender();
}
public Sender produceSms(){
return new SmsSender();
}
}
测试类如下:
public class FactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SendFactory factory = new SendFactory();
Sender sender = factory.produceMail();
sender.Send();
}
}
输出:
this is mailsender!
1.3、静态工厂方法模式,将上面的多个工厂方法模式里的方法置为静态的,不需要创建实例,直接调用即可。
public class SendFactory {
public static Sender produceMail(){
return new MailSender();
}
public static Sender produceSms(){
return new SmsSender();
}
}
public class FactoryTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sender sender = SendFactory.produceMail();
sender.Send();
}
}
输出:
this is mailsender!
总体来说,工厂模式适合:凡是出现了大量的产品需要创建,并且具有共同的接口时,可以通过工厂方法模式进行创建。在以上的三种模式中,第一种如果传入的字符串有误,不能正确创建对象,第三种相对于第二种,不需要实例化工厂类,所以,大多数情况下,我们会选用第三种——静态工厂方法模式。